Welcome to the first post in the ELK Stack series. Heard a lot about the power of Elasticsearch / ELK Stack. Experimenting with Elasticsearch was high on my to-do list. My use-case for this experiment is to put stock market buy / sell signals in to it and trying to query the market sentiment.
NOTE: Just documenting my experience and learning process, do not mind the mistakes and poor language skills.
Contents
What is Elasticsearch?
Elasticsearch is a system which allows you to save huge amounts of unstructured data into data sets (indexes). These indexes document based, which make querying them lighting fast. The Elasticsearch core is running on top off Apache Lucene. Apache Lucene is a java based indexing engine. The power of Elasticsearch is the REST Api which processes JSON Data and returning JSON data for each fired query.
How to Install Elasticsearch on Ubuntu Linux?
For my project I use a single instance Linux Ubuntu 18.4 virtual machine. Getting started with the java default-jre installation.
Install Java on Ubuntu Linux
First of all, check if Java not already installed on you system.
|
1 |
java --version |
If the output is looks like this “Command ‘java’ not found, but can be installed with”, install Java with the commands below.
|
1 2 |
sudo apt update sudo apt install default-jre |
Check your installation again.
Looks like mine is working.

Install Elasticsearch
Default Elasticsearch is not available in the official Ubuntu package repositories, so we need to add the source in our sources list. Before we do this we need to be sure that the right signing key is available on our system. Signing keys are used to protecting you from malicious packages which are spoofed.
Adding the signing key.
|
1 |
curl -fsSL https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add - |
Adding Elasticsearch sources.
|
1 |
echo "deb https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/7.x/apt stable main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-7.x.list |
Update package sources and install the Elasticsearch package.
|
1 2 |
sudo apt update sudo apt install elasticsearch |
Configure Elasticsearch
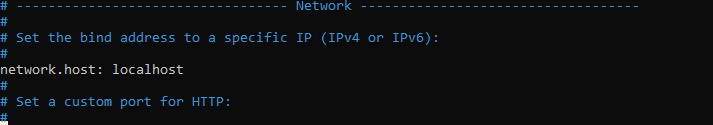
The Elasticsearch configuration file is mostly located in /etc/elasticsearch with the filename elasticsearch.yml. In this configuration file you can tweak the entire system. For our case we only use a Elasticsearch stand-alone server without clustering or other fancy features. To make sure our instance is listening on all interfaces we change the network binding to “localhost” in the configuration.
To change this network binding:
|
1 |
sudo nano /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml |
Remove the mark before network.host and change it to localhost.
Save it and restart the service.
|
1 2 |
sudo service elasticsearch stop sudo service elasticsearch start |
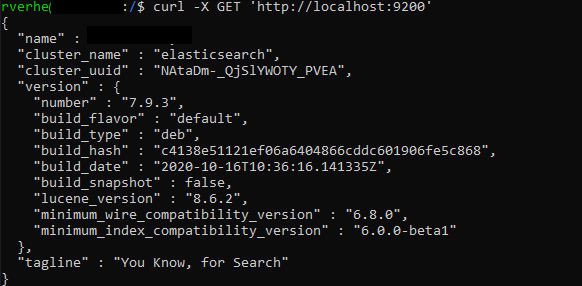
Test the installation with the following command:
|
1 |
curl -X GET 'http://localhost:9200' |